เบาหวาน แบ่งประเภทเป็น 4 ประเภทหลัก ๆ ขึ้นกับพันธุกรรม เมตาโบโลมิค และพยาธิสรีระวิทยา
1. Type 1 diabetes (เกิดจากออโตอิมมูนทำลายเบต้าเซลล์ของตับอ่อน autoimmune β-cell destruction) เกิดการขาดอินซูลินอย่างสิ้นเชิง มักพบในเด็ก แต่อาจเจอในผู้ใหญ่ได้ (latent autoimmune diabetes in adults) ลักษณะที่เข้าข่าย Type 1 ได้แก่ วินิจฉัยตั้งแต่อายุน้อย (<35 ปี), ดัชนีมวลกายต่ำ (BMI<25 kg/m2), น้ำหนักลดโดยไม่ได้ตั้งใจ, เลือดเป็นกรดจากคีโตน ketoacidosis, และน้ำตาลในเลือดสูง >360 mg/dL ครั้งแรกที่พบ
2. Type 2 diabetes (เกิดจากการสูญเสียการทำงานและการหลั่งอินซูลินจากเบต้าเซลล์ของตับอ่อนอย่างต่อเนื่อง โดยไม่ได้เกิดจากออโตอิมมูน nonautoimmune progressive loss of adequate β-cell insulin secretion เรียก ดื้ออินซูลิน insulin resistance)
3. เบาหวานที่มีสาเหตุจำเพาะ Specific types of diabetes เช่น ยีน monogenic diabetes syndromes, โรคตับอ่อน ยา สารเคมี เป็นต้น
4. เบาหวานระหว่างตั้งครรภ์ Gestational diabetes mellitus (diabetes diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy that was not clearly overt diabetes prior to gestation or other types of diabetes occurring throughout pregnancy, such as type 1 diabetes)
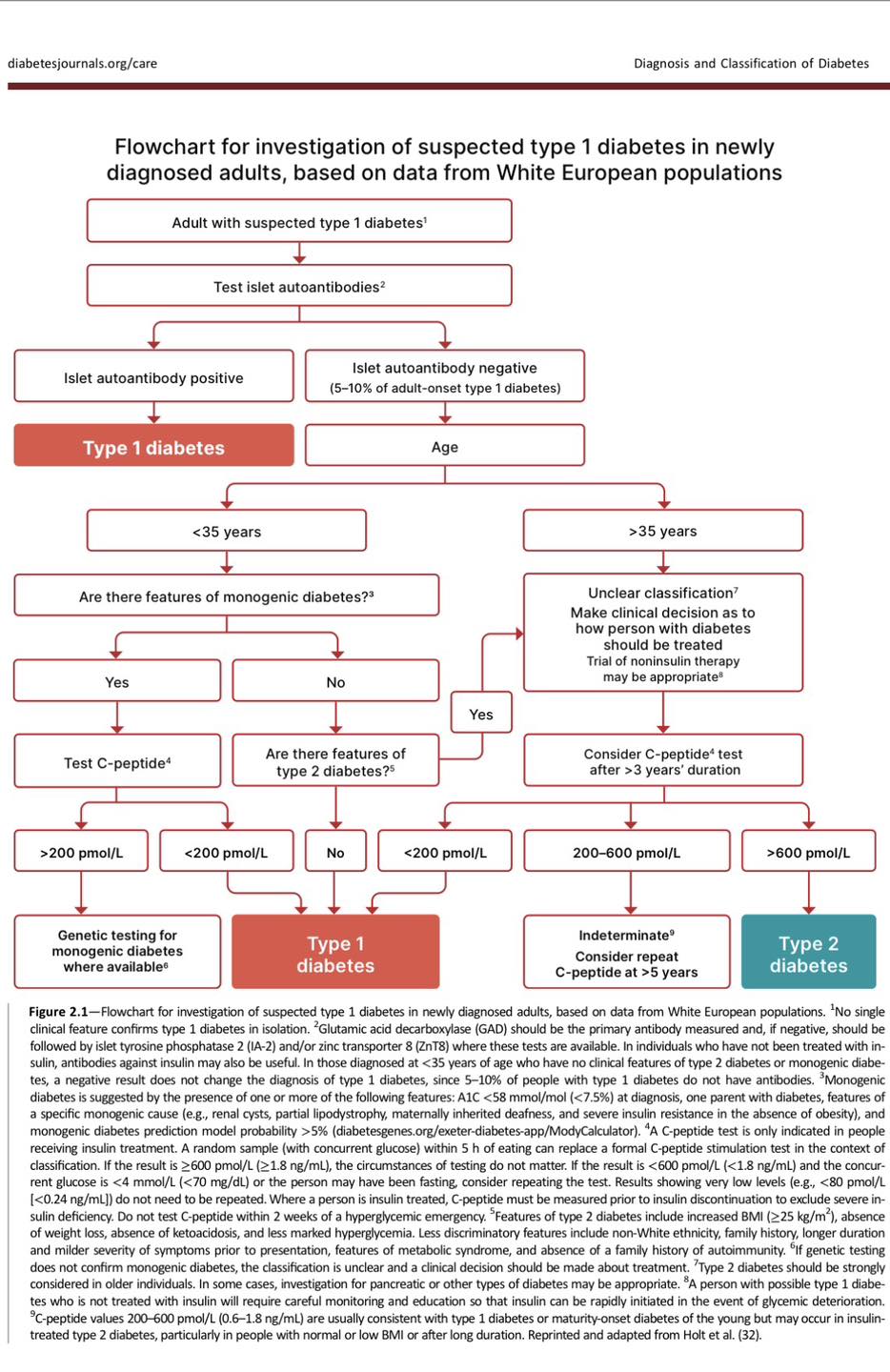
- เบาหวานชนิดที่ 1 และ 2 มีความแตกต่างกันทั้งอาการแสดงทางคลินิคและการดำเนินโรค การวินิจฉัยประเภทเบาหวานเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นต่อการรักษา
The AABBCC approach เป็นเครื่องมือช่วยแยกเบาหวาน type 1 และ type 2 ดังนี้ Age (e.g., for individuals <35 years old, consider type 1 diabetes); Autoimmunity (e.g., personal or family history of autoimmune disease or polyglandular autoimmune syndromes); Body habitus (e.g., BMI <25 kg/m2); Background (e.g., family history of type 1 diabetes); Control (preferred term is “goal,” i.e., the inability to achieve glycemic goals on noninsulin therapies); and Comorbidities (e.g., treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer can cause acute autoimmune diabetes)